Χημεία Σιλικονούχων Χρωμάτων
Η χημεία της σιλικόνης
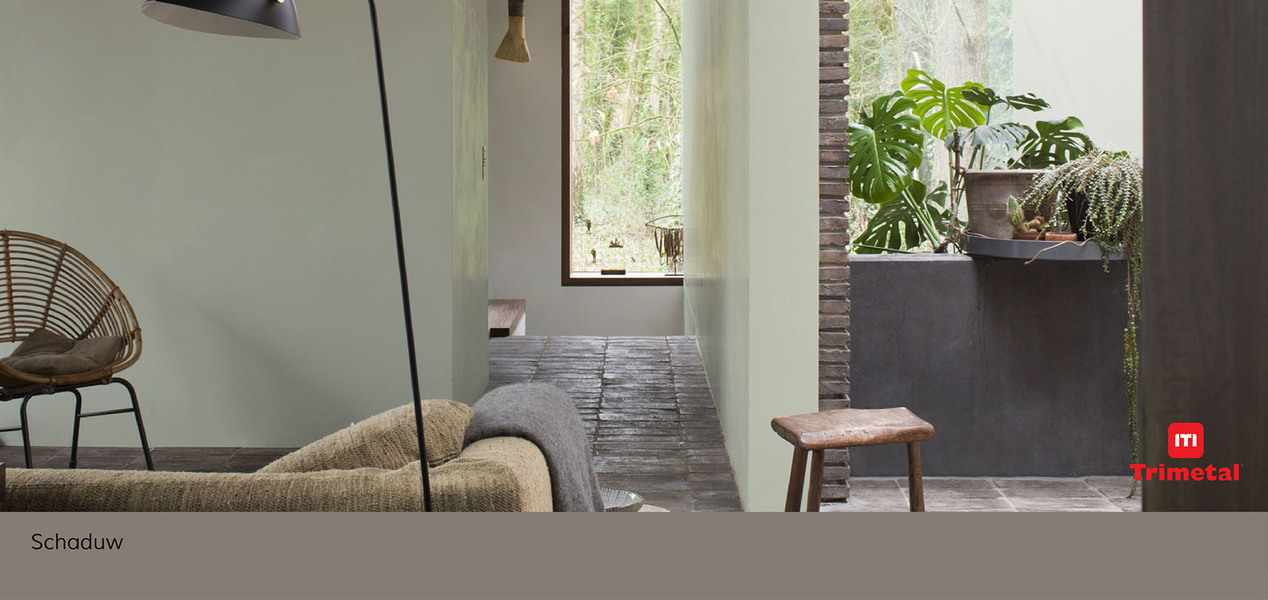
Οι σιλικόνες έχουν εξαιρετικές ιδιότητες
Σήμερα χρησιμοποιούνται σε πολλές διαφορετικές εφαρμογές. Τα προιόντα με σιλικόνη τα οποία είναι περισσότερα από 1000, χωρίζονται σε τρεις μεγάλες ομάδες: σιλικονούχα υγρά, σιλικονούχα ελαστομερή, και σιλικονούχες ρητίνες.
- Εξαιρετική αντοχής στις θερμοκρασίες από τις πολύ χαμηλές έως τις πολύ υψηλές
- Μακροχρόνια αντοχή
- Τέλεια ηλεκτρολογική μόνωση
- Τέλεια υδατοαπωθητικότητα, δίνοντας υδατοαπωθητικές ιδιότητες σε μια μεγάλη γκάμα από οργανικά και ανόργανα υποστρώματα
- Γενικά χαμηλή τοξικότητα
Ανάμεσα σε άλλες εφαρμογές οι σιλικόνες χρησιμοποιούνται σε γράσα, αντικολλητικές εφαρμογές, αντιαφριστικά, πρόσθετικά χρωμάτων, προσθετικά χαρτιού, μέσα εμποτισμού για δέρματα και κλωστουφαντουργία, και στην προστασία σκυροδέματος.
Ένα χρήσιμο δίκτυο δημιουργείται με το υλικό υπόστρωμα
Under the influence of moisture, silicone resin binders react with mineral construction materials by way of a catalyzed condensation reaction to form a silicone resin network. Bound alcohol is split off during the process. All masonry protection measures involving the use of silicones are based on the formation of this network, which binds chemically to the mineral substrate and makes it water repellent but permeable to water vapor.

- Silicone resin network formation
The three-dimensionally crosslinked structures of silicone resin, quartz, water glass and ethyl silicate are related. Silicone resin has a quartz structure permanently modified with hydrophobic organic groups R. In the case of water glass (modified with potassium salt, Si-O−K+) ethyl silicate (modified with ethanol, (Si−OEt), the modificiation of the quartz structure is reversible.
Unlike silicone resin, both these substances can undergo a silicification reaction, eliminating the modifier (potassium carbonate after reaction with atmospheric carbon dioxide in the case of water glass, and ethanol after reaction with water in the case of ethyl silicate) to yield, once more, pure silicon dioxide (SiO2)
Silicone resins are high-molecular, three-dimensionally crosslinked compounds that are based – like quartz – on a silicon/oxygen skeleton. Unlike quartz, however, every fourth oxygen atom of a silicone resin is replaced by an organic group R. It can therefore be described as an organically modified quartz structure. All silicone resins consist of 30 to 80 trifunctional silicon-T units with molecular weights of 2,000 to 5,000 – which is very low compared to organic resins. They also contain 2 to 4 wt. percent of residual alcohol. Chemically speaking, silicone resins form an intermediate class between purely inorganic and purely organic substances.
Silicone resins are formed by polycondensation of silanes. During this reaction, viscous and solid polymeric siloxanes (referred to as liquid and solid resins) are formed, which are soluble in organic solvents. These silicone resins – almost exclusively methyl silicone resins – are used as binders in silicone resin paints and silicone resin plasters.
Methyl silicone resins dry from organic solution or emulsion to form a non-tacky film, which is already fully water-repellent. In a process referred to as chemisorption, the remaining alcohol groups undergo a condensation reaction with available substrate groups (usually OH−), forming silanol; the alcohol groups also react with one another, thus further crosslinking the silicone resin into a silicone resin network .
Silicone resin binders
For the formulation of silicone resin emulsion paints according to DIN 18363, the silicone resins are used in the form of aqueous emulsions. These emulsions may be solvent-free or solvent-based, depending on how they are produced. Solvent-free emulsions are prepared by emulsion polycondensation of liquid silicone resin or by emulsifying a silane/siloxane/silicone resin mixture. Solvent-based emulsions are prepared by dissolving solid silicone resin in organic solvents and then emulsifying the solutions. Silanes, siloxanes and siliconates are also classified as silicone resins because they form silicone resin networks on mineral surfaces. These products are referred to collectively as silicone masonry protection agents.
The excellent results obtained with silicone resin emulsion paints for more than forty years now are due to the use of silicone resin as binder. Attempts to replace three-dimensionally crosslinking silicone resins with low-cost, simple chain-forming silicone fluids will inevitably fail in the long run, since these products are entirely devoid of any pigment-binding power.
The invention
Silicone resin emulsion paint was developed in WACKER’s laboratories forty years ago, and a patent application was filed by the three researchers Siegfried Nitzsche, Ewald Pirson and Michael Roth. This made WACKER the first company to introduce silicones for masonry protection, and the global market leader in this field. Incidentally, the paint was initially called “Munich paint.”
As the most advanced modern facade coating systems, silicone resin emulsion paints enjoy widespread acceptance in Europe, and they are also being used increasingly to treat construction objects in the USA, Singapore and Japan. Almost every manufacturer of exterior paints includes these products in its range.
The patent
“The invention relates to coating materials based on aqueous dispersions of organopolysiloxanes and an organic resin content, said organic content, however, not exceeding the organopolysiloxane content. The coating materials according to the invention provide washable, chalking-resistant coatings, which have high water repellency and weathering resistance and outstanding permeability to air and water vapor.”